By January 2026, there are still 270 active drug shortages in the U.S.-and nearly all of them are generic medications. These aren’t rare or obscure drugs. They’re the ones hospitals and pharmacies rely on every day: antibiotics like vancomycin, chemotherapy agents like cisplatin, IV fluids like saline, and even basic painkillers. When these drugs disappear from shelves, it’s not just an inconvenience. It’s a direct threat to patient safety.
Why Do Generic Drugs Keep Running Out?
Generic drugs make up 90% of all prescriptions filled in the U.S., but they account for more than 70% of all shortages. Why? Because the business model doesn’t support reliability. Manufacturers make razor-thin profits-sometimes just 5% to 10% gross margin-on these drugs. Compare that to brand-name drugs, which can earn 30% to 40%. When the profit is this small, companies have little incentive to invest in backup equipment, extra inventory, or high-quality manufacturing. One machine breaks down? No spare parts. One supplier has a quality issue? No alternative source. And because many of these drugs have only one or two FDA-approved makers, the whole system collapses with a single failure.The Sterile Injectables Crisis
Sterile injectables are the most vulnerable category. About 60% of all drug shortages involve these medications-things like antibiotics given through IV, anesthetics, and cancer drugs. Why? Because making sterile injectables requires clean rooms, specialized equipment, and strict controls. One tiny contamination can shut down an entire production line for months. And these drugs are often made in just one or two factories worldwide. Over 80% of the active ingredients in U.S. drugs come from China and India. A single inspection failure, power outage, or regulatory delay in one overseas facility can ripple across the entire American healthcare system.How Shortages Hurt Patients
When a drug vanishes, doctors don’t just prescribe something else. They scramble. A 2022 survey found that 63% of pharmacists saw serious patient harm because of shortages. Cancer patients get delayed treatments. Diabetics can’t get insulin. People with chronic pain go without medication because the only affordable option is out of stock. In one hospital, vancomycin powder for reconstitution was gone for eight months. Staff had to switch to more expensive, less effective alternatives-and patients paid the price in longer hospital stays and higher infection rates.Price Spikes and Abandoned Prescriptions
When a generic drug runs out, the price doesn’t just go up-it explodes. The median price increase for a shortage drug is 14.6%, but substitute drugs can jump three times that rate. Independent pharmacies report that 43% of patients simply give up on their prescriptions because they can’t afford the new cost. A patient who’s been taking a $2 generic blood pressure pill might suddenly face a $60 alternative. That’s not a choice-it’s a forced decision between health and rent.
Healthcare Workers Are Overwhelmed
Pharmacists aren’t just filling prescriptions anymore. They’re full-time shortage detectives. On average, they spend 15 to 20 hours a week tracking down alternatives, updating electronic systems, and retraining staff. That’s time stolen from patient consultations, medication reviews, and safety checks. Hospitals report that drug shortages make existing staffing crises worse. In 2025, 72% of hospitals said shortages increased burnout and turnover among pharmacy teams. Meanwhile, clinics spend an average of 12.3 hours per week just trying to find a single drug. The American Hospital Association estimates the U.S. spends $213 million a year just managing this mess.Why Brand Drugs Don’t Have the Same Problem
Brand-name drugs still have shortages-but far fewer. Why? Because they’re protected by patents and pricing power. Companies can raise prices, invest in backup manufacturing, and maintain higher inventory levels. Generic manufacturers can’t. They compete on price alone. And when you’re bidding against other companies to sell a $0.10 pill, quality and reliability are the first things to get cut. Between 2018 and 2023, there were 1,391 shortages of generic drugs versus just 600 for brand-name drugs-even though generics make up 90% of prescriptions.The Manufacturing Exodus
The number of FDA-registered generic drug manufacturing facilities in the U.S. dropped 22% between 2015 and 2024-from 1,842 to just 1,437. Why? Because it’s cheaper to make drugs overseas, even with shipping and regulatory hurdles. But that’s made the system brittle. If a factory in India shuts down for a quality audit, there’s no U.S.-based backup. And as the top 10 generic manufacturers now control 60% of the market, competition has shrunk. Fewer players means less innovation, less redundancy, and more risk.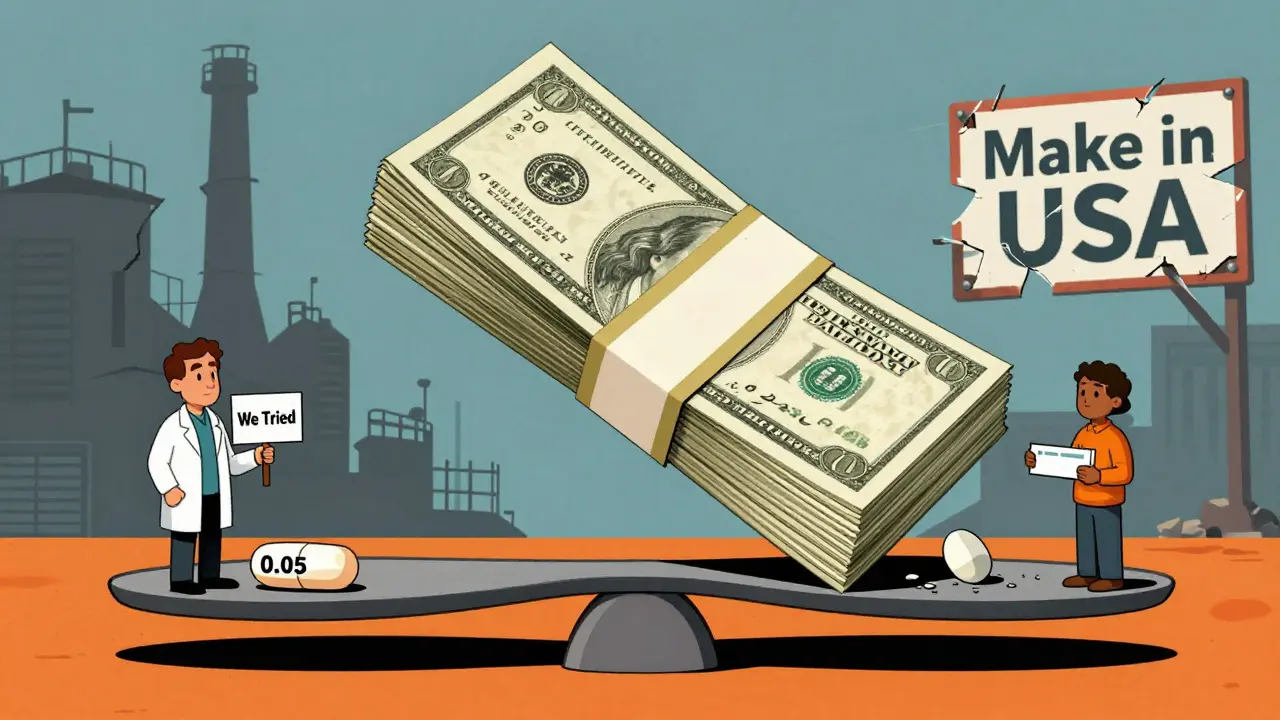





Crystel Ann
January 14, 2026 AT 23:39This is the quiet crisis no one talks about until someone’s loved one can’t get their chemo or insulin. I’ve seen pharmacists cry because they can’t help a diabetic patient who can’t afford the $70 substitute. It’s not about politics-it’s about people being forced to choose between medicine and groceries.
Nat Young
January 16, 2026 AT 05:30Let’s be real-this whole ‘generic drug shortage’ narrative is just Big Pharma’s way of pushing you toward more expensive brand-name pills. You think they don’t profit from this chaos? They own the patents, they own the alternatives, and they’ve been lobbying against price controls for decades. The real villain isn’t the manufacturer-it’s the monopoly system that lets them play god with life-saving meds.
Niki Van den Bossche
January 16, 2026 AT 13:20Ah, the tragic ballet of capitalist decay-where the very substances that sustain biological equilibrium are reduced to commodities traded on a deranged auction floor. We’ve commodified the sacred: the IV drip, the antibiotic vial, the insulin pen-all rendered expendable by the cold calculus of marginal utility. The soul of medicine, once a covenant between healer and healed, now flickers like a dying monitor in a warehouse in Chennai. We are not merely failing patients-we are erasing the moral architecture of care.
Iona Jane
January 16, 2026 AT 23:01Did you know the FDA is controlled by a shadow consortium of pharmaceutical CEOs? They allow these shortages on purpose so they can jack up prices on the ‘alternatives’-which are just rebranded generics with a new label. The power outages in India? Staged. The inspections? Fraud. The ‘emergency’? A profit trigger. They want you dependent on their $60 pills. Don’t be fooled.
Jaspreet Kaur Chana
January 18, 2026 AT 11:27As someone from India, I’ve seen firsthand how these factories operate-hundreds of workers in clean rooms, no overtime pay, machines running 24/7 because the orders never stop. The problem isn’t just greed-it’s globalization without accountability. We make the drugs, we bear the pollution, we take the blame when things break, but the profits flow to Wall Street and the CEOs in New Jersey. We need fair wages, better inspections, and real partnerships-not just export orders. This isn’t just America’s crisis-it’s ours too, and we’re tired of being the invisible backbone of your healthcare.
Haley Graves
January 19, 2026 AT 20:57If you’re on a generic med, talk to your pharmacist now-not next month. Ask about alternatives, patient assistance programs, even mail-order options. You’re not powerless. And if you’re a nurse, doctor, or pharmacist-speak up at your hospital meetings. This isn’t just policy-it’s daily survival. Your voice matters. Start small. Document. Share. Push. Change happens when people stop being silent.
Gloria Montero Puertas
January 21, 2026 AT 05:34Of course, the ‘solution’ is to pay more… but who? The uninsured? The Medicare recipient? The underpaid nurse? You want manufacturers to invest? Fine-then eliminate the middlemen: PBMs, insurers, hospital procurement departments. Let manufacturers sell directly to patients at cost-with a 20% margin. No bidding wars. No ‘lowest price wins.’ No profit-driven neglect. And if you think this is radical, ask yourself: why is a $0.05 pill worth more to Wall Street than a human life?
Frank Geurts
January 22, 2026 AT 01:22While the systemic challenges outlined in this exposition are indeed profound and warrant immediate policy recalibration, it is imperative to acknowledge that the root cause lies not merely in profit margins, but in the absence of a federally mandated strategic reserve for essential generic pharmaceuticals-a model successfully employed for critical medical equipment during the pandemic. Furthermore, the current regulatory framework lacks the requisite fiscal incentives for domestic re-manufacturing infrastructure. A public-private partnership, underwritten by a modest excise tax on brand-name drug profits, could catalyze the revival of U.S.-based sterile production facilities, thereby mitigating geopolitical supply chain vulnerabilities. The time for incrementalism has expired; what is required is a paradigmatic shift in national health security policy.